Introduction
The evolution of data centers and cloud networks has been driven by the demand for higher bandwidth, lower latency, and scalable interconnections. Among the various standards, the 400G DR4 optical module has been widely adopted. Designed according to the IEEE 400GBASE-DR4 specification, it provides cost-effective, power-efficient, and high-performance connectivity for next-generation networks.
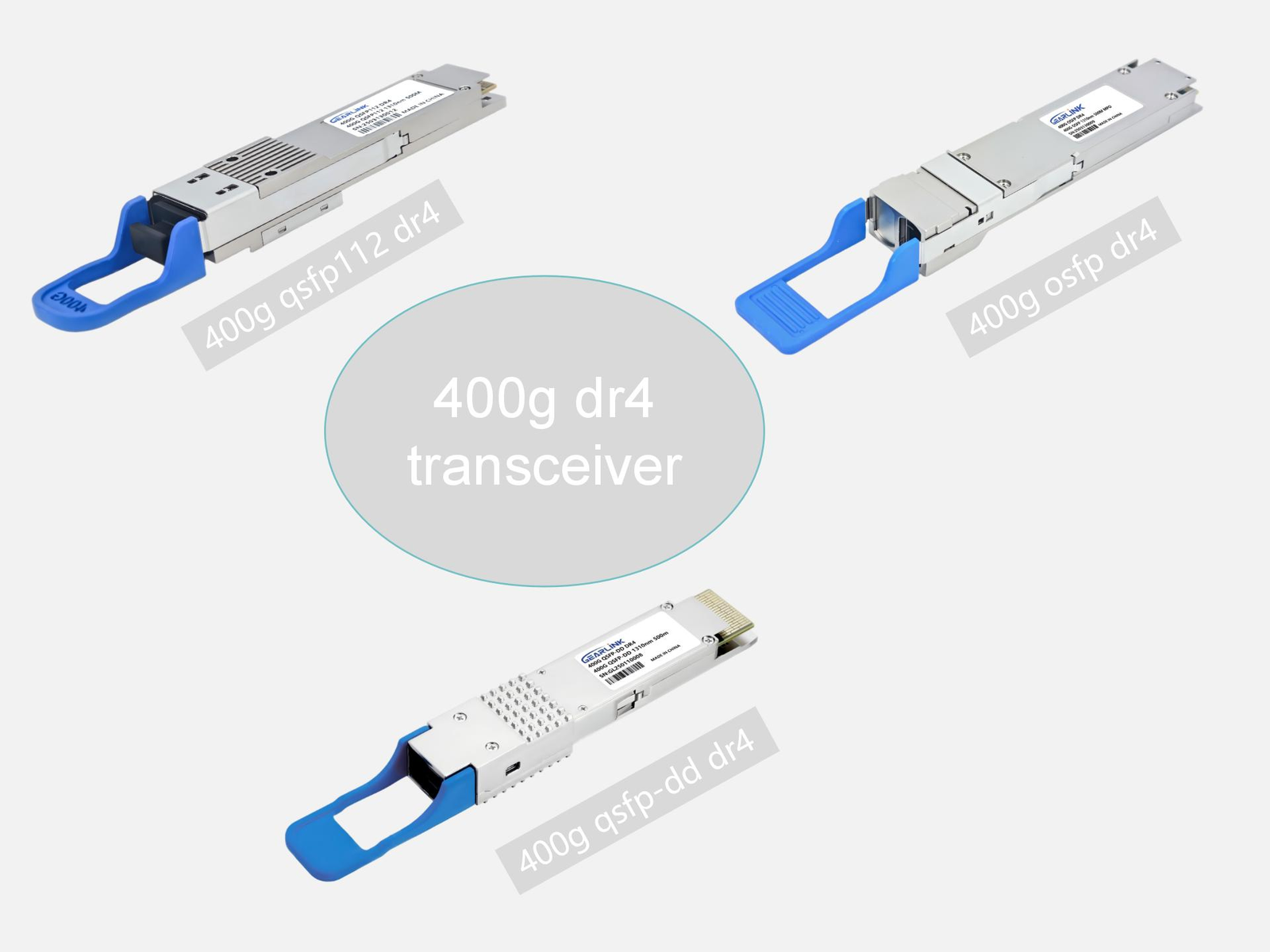
The 400G DR4 transceiver is built primarily in the QSFP-DD (Quad Small Form Factor Pluggable Double Density) form factor, but versions in OSFP and QSFP-DD are also available to meet different vendor requirements.
What Is a 400G DR4 Transceiver?
A 400G DR4 transceiver is an optical module that supports 400Gbps Ethernet or IB transmission over parallel single-mode fiber. It uses 4 parallel lanes of 100G PAM4 signaling, transmitted and received via an MPO-12/APC connector. The “DR” in DR4 stands for “Data Rate” with a reach of 500 meters on single-mode fiber (SMF), which makes it highly suitable for large-scale data centers.
Compared to other optical standards, 400G DR4 offers a balance of affordability, scalability, and interoperability.
400G DR4 Specifications and Standards
400GBASE-DR4 OSFP PAM4 1310nm 500m DOM MPO-12/APC SMF Optical Transceiver Module
Price range: NT$699 through NT$799
According to the IEEE 802.3bs standard, the 400GBASE-DR4 specification defines the following characteristics:
Data Rate: 400Gbps
Interface: QSFP-DD, OSFP, QSFP112
Connector Type: MPO-12/APC
Optical Reach: Up to 500m over single-mode fiber
Breakout Support: 4 × 100G connections (to 100G DR1 modules)
Compliance: MSA standards such as 400G DR4 MSA
This means that a single 400G DR4 transceiver can either be deployed as a 400G link or broken out into 4 × 100G DR1 links, providing flexible connectivity for leaf-spine architectures.
400G DR4 Connector Types and Breakout Options
One of the defining features of the 400G DR4 module is its use of an MPO-12/APC connector. This multi-fiber push-on connector allows for parallel optics transmission.
400G DR4 Breakout: The module can break out a single 400G port into four 100G DR1 ports, which is essential in data centers where 400G switches need to interconnect with existing 100G infrastructure.
Compatibility: The breakout is supported across Cisco, Arista, Juniper, and other networking vendors, making the technology widely deployable.
400G DR4 vs 400G FR4: Understanding the Difference
A frequent question is the difference between 400G DR4 and 400G FR4.
400G DR4: Uses 4 parallel 100G lanes on single-mode fiber; reach up to 500m.
400G FR4: Uses CWDM4 technology with 4 wavelengths multiplexed; reach up to 2km.
Thus, 400G DR4 transceivers are usually preferred for intra–data center connectivity, while FR4 modules are deployed for slightly longer interconnections.
400G DR4 Transceiver Applications
The adoption of 400G DR4 optics has been seen across hyperscale data centers and enterprise networks.
Data Center Interconnect (DCI)
AI/ML clusters requiring ultra-low latency
Spine-leaf architectures where 400G-100G breakout is needed
Cloud service providers for bandwidth expansion
The 400G DR4 optical transceiver provides scalability by allowing easy migration from 100G DR1 to 400G DR4 without significant infrastructure changes.
400G DR4 Transceiver in QSFP-DD and OSFP Form Factors
Most 400G DR4 modules are manufactured in the QSFP-DD form factor due to its backward compatibility with existing 100G/200G optics. However, OSFP DR4 versions are also available, providing improved thermal performance and supporting future 800G scalability.
Both form factors follow the 400GBASE-DR4 IEEE standard, but vendor preferences may dictate which is deployed.
Vendor-Specific 400G DR4 Solutions
Different networking equipment providers have integrated 400G DR4 transceivers into their platforms:
Cisco 400G DR4-S: Offers seamless breakout to 4 × 100G and supports Cisco Nexus switches.
Arista 400GBASE-DR4: Designed for Arista 7060X4 and 7800R3 series switches.
Juniper QSFP56-DD-400GBASE-DR4: Optimized for Juniper’s QFX and PTX platforms.
These implementations ensure that 400G DR4 optical modules are interoperable across multi-vendor environments.
400G DR4 Price and Market Trends
The price of 400G DR4 transceivers has been gradually decreasing as adoption rises. Initially priced at several thousand dollars per unit, the cost has dropped significantly due to high-volume manufacturing and competition among vendors.
Compared to 400G FR4 modules, DR4 optics are typically more affordable because they do not require complex wavelength multiplexing. This makes them an attractive choice for hyperscale deployments.
400G DR4 Cable and Connectivity
Besides optical modules, 400G DR4 cables are also available:
Active Optical Cables (AOC) for plug-and-play deployments
Breakout Cables (400G to 4 × 100G) using MPO-LC fanout
Direct Attach Cables (DAC) for short-reach connections
These solutions extend the versatility of 400G DR4 transceivers in real-world network deployments.
400GBASE-DR4 and IEEE Standards
The IEEE 802.3bs 400GBASE-DR4 standard ensures interoperability across vendors. It defines not only the physical layer but also compliance testing, power consumption, and optical characteristics.
Additionally, MSA groups have published guidelines to extend compatibility, such as the DR4 MSA for breakout operations.
400G DR4 vs 400G DR4-2
There are variations of 400G DR4, including 400GBASE-DR4-2, which uses 8 parallel 50G lanes instead of 4 × 100G lanes. While DR4-2 offers flexibility in certain scenarios, 400G DR4 remains the mainstream choice for 400G deployments.
Future of 400G DR4 and Beyond
As the industry moves toward 800G and 1.6T transceivers, the legacy of 400G DR4 transceivers will remain critical for backward compatibility. Many next-generation modules will support DR8 or FR8, which are essentially evolutions of DR4 technology.
Thus, investing in 400G DR4 optics today ensures a smoother migration path toward future architectures.
Conclusion
The 400G DR4 transceiver has emerged as one of the most practical and scalable solutions for high-speed data center interconnections. Its compliance with IEEE 400GBASE-DR4, support for MPO-12 connectors, cost-effectiveness compared to other 400G standards, and wide vendor adoption make it an essential technology for modern networking.
As hyperscale operators and enterprises continue to scale their networks, 400G DR4 optical modules will remain at the core of reliable, efficient, and future-ready connectivity.
FAQ
1. What is a 400G DR4 transceiver?
A 400G DR4 transceiver is an optical module that delivers 400Gbps Ethernet or IB using 4 × 100G lanes over single-mode fiber, with a maximum reach of 500m.
2. What connector type is used in 400G DR4 optics?
The 400G DR4 transceiver uses an MPO-12/APC connector, enabling parallel optical transmission and support for breakout to 4 × 100G DR1 links.
3. What is the difference between 400G DR4 and 400G FR4?
400G DR4 supports 500m reach with parallel optics, while 400G FR4 uses multiplexed wavelengths to reach up to 2km.
4. Can 400G DR4 modules be used with Cisco, Arista, and Juniper switches?
Yes. Major vendors like Cisco, Arista, and Juniper all support 400GBASE-DR4 modules for data center interconnections.
5. What is the typical price of a 400G DR4 transceiver?
The price has decreased significantly with mass adoption, making 400G DR4 optics one of the most cost-effective solutions for high-speed connectivity.