With the continuous growth of data centers, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence, the demand for network bandwidth has been significantly increased. The 400G optical transceiver has been established as the mainstream solution for next-generation core interconnects. Whether Cisco 400G transceivers or widely adopted modules such as QSFP-DD 400G DR4/FR4/LR4, they are all driving the upgrade of high-speed Ethernet. In this article, the 400G optical transceiver is thoroughly explained in terms of definition, major types, application scenarios, price and cost, as well as typical product models such as QDD-400G-SR8-S and QSFP-400G-DR4. By doing so, enterprises can better understand and select the proper solution.
What is a 400G Optical Transceiver?

A 400G optical transceiver is defined as a high-speed optical module that supports 400 Gigabit Ethernet (400GbE). It is primarily applied in data center interconnect (DCI), AI clusters, large-scale cloud networks, and telecom backbones.
Its function is realized by converting electrical signals into optical signals for transmission and converting optical signals back into electrical signals at the receiving end. Compared with traditional 100G or 200G modules, the 400G optical transceiver offers remarkable advantages in bandwidth, energy efficiency, and port density.
How Does a 400G Optical Transceiver Work?
Inside the module, high-speed DSP chips, lasers, and photodetectors are integrated.
On the transmitting side: electrical signals from the switch or server are converted into optical signals and transmitted through fiber.
On the receiving side: incoming optical signals are converted back into electrical signals before being returned to the switch.
In this way, the 400G optical transceiver is regarded as the essential “electro-optical converter” in high-speed Ethernet systems.
Standards and Form Factors of 400G Optical Transceivers
400G Ethernet Standards
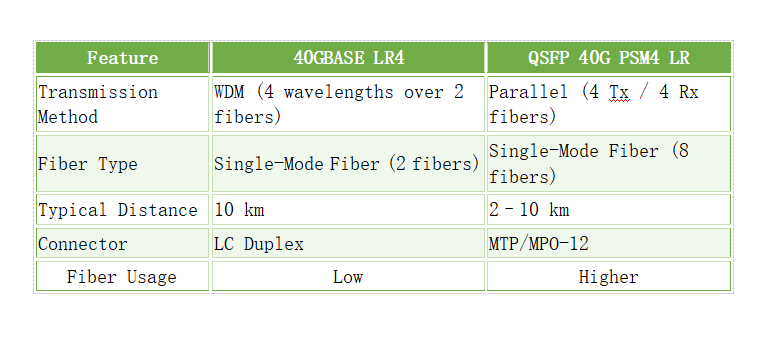
The 400G Ethernet standard was defined by IEEE 802.3bs. The most common interfaces include:
400G SR4: based on multimode fiber, up to 500 meters.
400G DR4: based on single-mode fiber, up to 500 meters.
400G FR4: 4-wavelength multiplexing, up to 2 kilometers.
400G LR4: long-reach, up to 10 kilometers.
By these standards, compatibility and interoperability between different vendors are guaranteed.
Common Form Factors
QSFP-DD 400G (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable Double Density): the most widely adopted, highly compatible, used in Cisco 400G optics, Arista, Juniper, and others.
OSFP 400G (Octal Small Form-factor Pluggable): designed for larger power consumption and better heat dissipation.
CFP8 400G: an early standard, gradually replaced by QSFP-DD.
Currently, the QSFP-DD 400G optical transceiver has been regarded as the first choice for modern data centers.
Cisco 400G Transceivers and Typical Products
400GBASE-DR4 OSFP PAM4 1310nm 500m DOM MPO-12/APC SMF Optical Transceiver Module
Price range: NT$699 through NT$799
As a global leader, Cisco 400G optics are widely deployed in enterprise networks and hyperscale data centers. Several mainstream product models have been released:
QDD-400G-SR8-S: designed for multimode fiber, supporting 70–100 meters for short-reach interconnects.
QDD-400G-DR4-S: a single-mode solution for up to 500 meters, suitable for rack-to-rack connections.
QSFP-400G-FR4: designed for 2 km applications, ideal for campus or building-to-building interconnects.
QSFP-400G-LR4: capable of 10 km transmission, widely used in metro networks.
These modules differ significantly in terms of Cisco 400G QSFP price. Short-distance transceivers are available at lower cost, while long-distance LR4 modules are more expensive.
400G Optical Transceiver Price and Cost
The 400g optical transceiver price has been frequently considered during procurement.
Factors Influencing Cost
Transmission distance: SR8 < DR4 < FR4 < LR4.
Form factor: QSFP-DD is usually lower in cost than OSFP.
Brand: original Cisco modules are higher in cost, while third-party compatible modules are more affordable.
Purchase scale: bulk procurement greatly reduces the average price.
Cisco 400G Transceiver Price Range
QDD-400G-SR8-S: priced from several thousand RMB.
QSFP-400G-DR4: priced from high thousands RMB.
QSFP-400G-FR4/LR4: generally above ten thousand RMB.
Therefore, the 400g optical transceiver cost varies significantly depending on the application scenario.
Application Scenarios of 400G Optical Transceivers
Intra-Data Center Connections
400G DR4 modules are mainly deployed for rack-to-rack connectivity within 500 meters.
400G SR8 is usually applied between Top-of-Rack (ToR) switches and aggregation switches.
Data Center Interconnect (DCI)
400G FR4 supports up to 2 km, ideal for campus and short DCI links.
400G LR4 enables 10 km transmission, supporting metro-level connections.
AI and High-Performance Computing (HPC)
With the rapid expansion of AI training clusters, requirements for low latency and high bandwidth have been intensified. The QSFP-DD 400G optical transceiver has been deployed for high-density ports, becoming the first choice in AI-driven data centers.
Comparison Between 400G and Other Optical Transceivers
400G vs 100G/200G
Bandwidth: 400G = 4 × 100G.
Energy efficiency: lower power per Gbps.
Port density: higher density reduces cabling complexity.
400G vs 800G
400G optical transceiver solutions are still dominant, with mature ecosystem support.
800G optical modules are emerging, especially for AI superclusters, but 400G remains the practical mainstream.
Conclusion
The 400G optical transceiver has been positioned as the cornerstone of next-generation networks. With products such as QDD-400G-SR8-S, QSFP-400G-DR4, QDD-400G-DR4-S datasheet-based solutions, and Cisco 400G transceivers, enterprises are empowered to build high-performance, future-proof networks. As the demand for Cisco 400G optics continues to expand, price optimization and application-driven deployment will remain the key considerations.
FAQ
Q1: Which transceivers can support 400 Gigabit Ethernet?
A1: Several models such as QSFP-DD 400G DR4, QSFP-400G-FR4, QSFP-400G-LR4, and QDD-400G-SR8-S are designed to support 400G optical transceiver solutions for 400 Gigabit Ethernet.
Q2: What is the difference between 400G FR4 and 400G LR4?
A2: The 400G FR4 module is designed for up to 2 km transmission, while the 400G LR4 module is specified for up to 10 km. Both belong to the Cisco 400G optics family and are commonly deployed in different distance scenarios.
Q3: What does a 400G optical transceiver do?
A3: A 400g optical transceiver is used to convert electrical signals into optical signals for transmission over fiber, and then convert them back into electrical signals at the receiving end, enabling high-speed data transfer in Cisco 400G transceivers and other platforms.
Q4: Are transceiver and SFP the same?
A4: No. A transceiver is a general term for modules like the 400g optical transceiver, while SFP, QSFP, and QSFP-DD are specific form factors. For example, QSFP-DD 400G optical transceiver is one of the most common standards today.
Q5: What is the price range of a 400G optical transceiver?
A5: The 400g optical transceiver price varies by type. Short-reach models such as QDD-400G-SR8-S are available at lower cost, while longer-reach modules like QSFP-400G-LR4 are priced higher. The Cisco 400G QSFP price is generally above compatible third-party alternatives.