High-speed interconnect optical transceivers play a critical role in the deployment of AI computing and high-performance data centers. In this article, we’ll explore the product features, application scenarios, and deployment methods of the 800G OSFP 2×SR4 and 400G OSFP SR4 optical transceivers in NVIDIA 9790/9700 switches and CX7 network interface cards (NICs), and examine the optical transceiver requirements in a Leaf-Spine network architecture.
1. Overview of 800G OSFP 2×SR4 Optical Transceiver
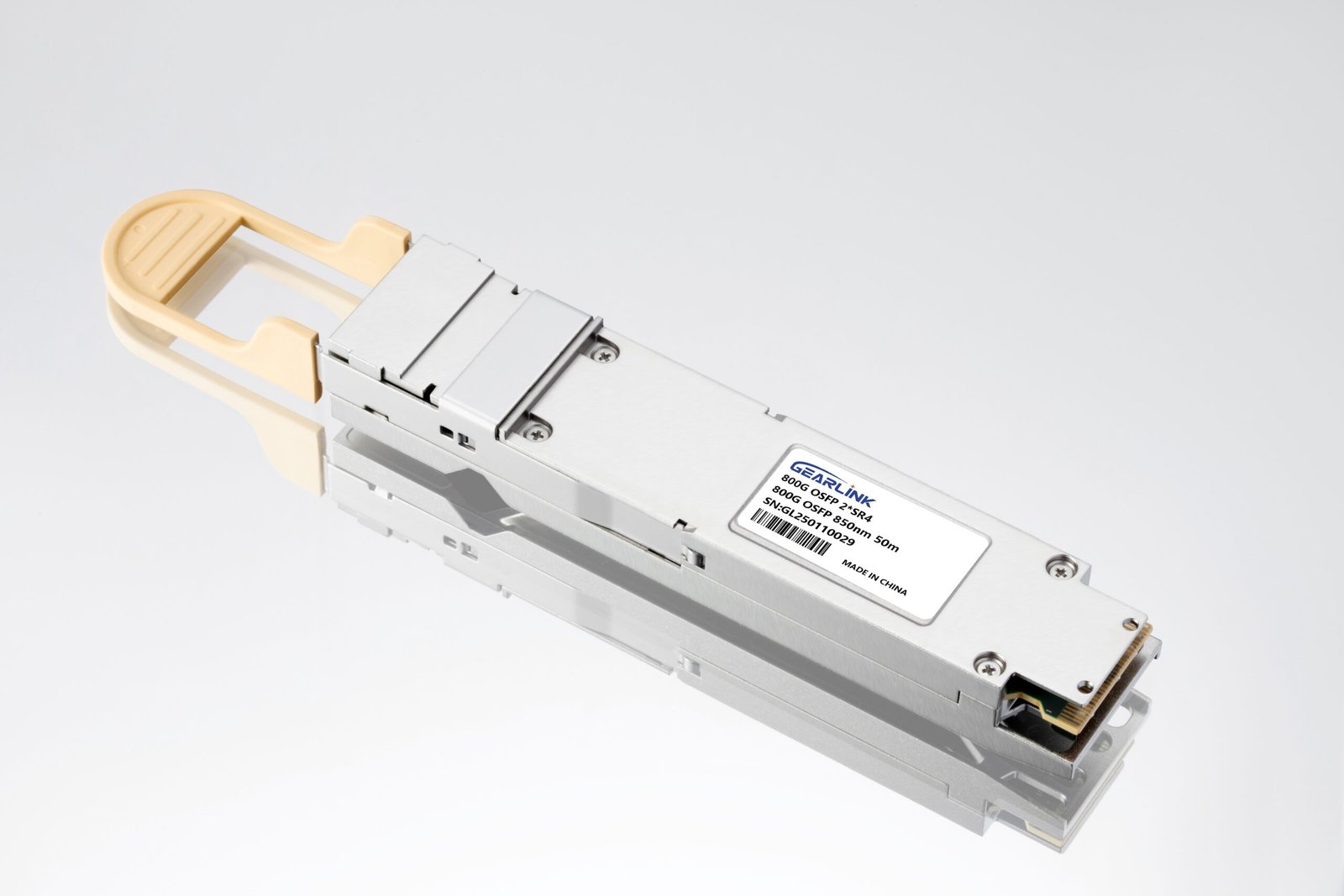
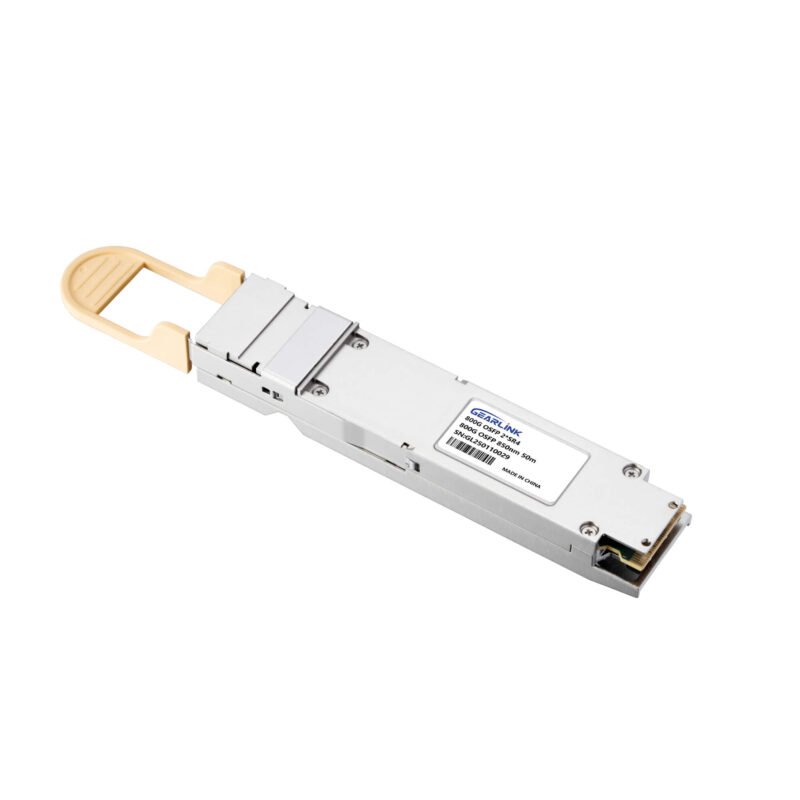
Product Description:
- Based on 2×400G SR4 design, utilizing an 8×100G (PAM4) rate scheme.
- Uses MPO-12 connectors, suitable for short-distance parallel optical interconnects.
- Mainly used for Spine-Leaf switch interconnection, supporting AI computing clusters and high-performance data centers.
Key Features:
- High Bandwidth: Supports 800G transmission, meeting AI computing demands.
- Low Power Consumption: Optimized circuit design for improved energy efficiency.
- High Reliability: Stable PAM4 signal modulation technology reduces bit error rate.
- Thermal Optimization: Finned top design for heat dissipation, suitable for high-density switch environments.
Application Scenarios:
- Spine-to-Leaf switch interconnection in data centers.
- High-speed data transmission in AI computing clusters.
- Hyperscale high-performance computing (HPC) infrastructures.
2. Overview of 400G OSFP SR4 Optical Transceiver
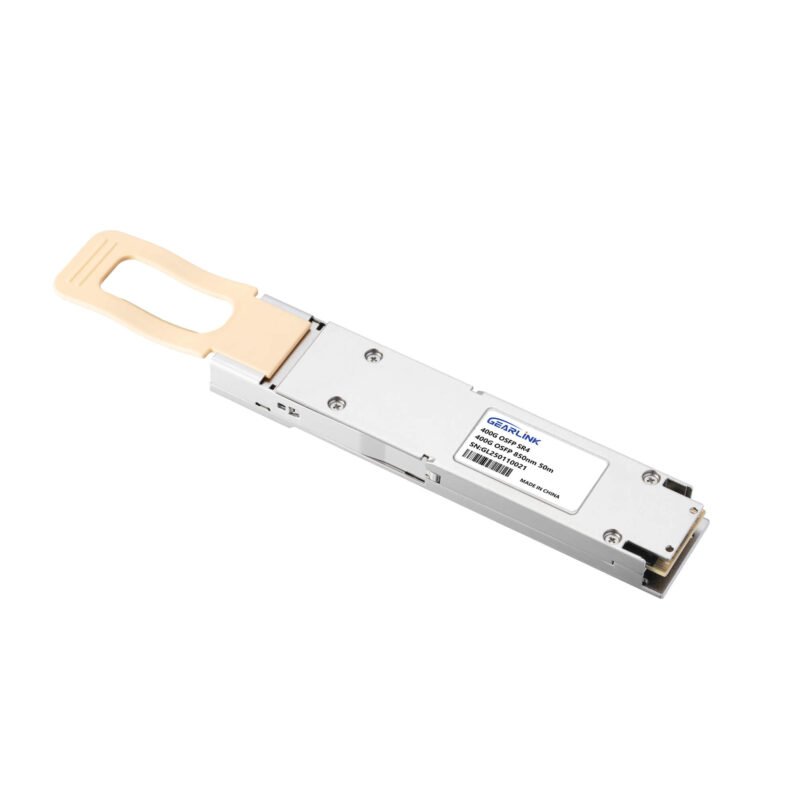
Product Description:
- Based on the 400G SR4 design with a 4×100G (PAM4) transmission scheme.
- Uses MPO-12 connectors for short-distance, high-bandwidth transmission.
- Primarily used for connecting servers (CX7 NICs) to Leaf switches.
Key Features:
- High Performance: Delivers stable 400G interconnect performance.
- Low Power Design: Optimized circuitry and transmitter efficiency.
- Strong Compatibility: Fully compatible with NVIDIA CX7 NICs for seamless connectivity.
- Flat Top Design: No heatsink required as the CX7 NIC has its own thermal solution.
Application Scenarios:
- Connections between servers (CX7 NICs) and Leaf switches.
- GPU server interconnects in AI computing clusters and high-performance data centers.
- High-throughput links in large-scale distributed computing environments.
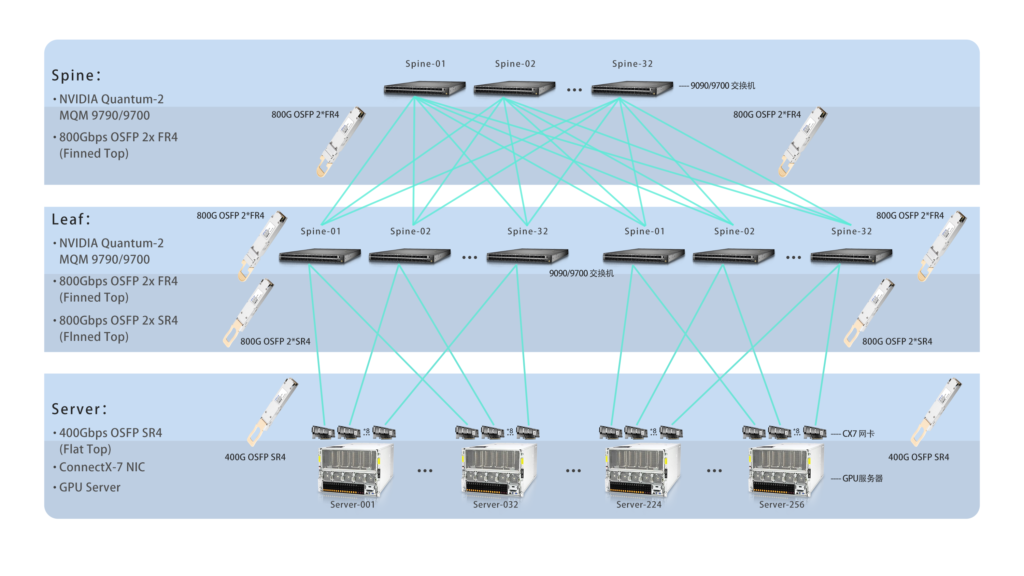
3. Leaf-Spine Architecture and Optical Transceiver Deployment
Introduction to Leaf-Spine Architecture:
- Adopts a scale-out model to enhance network throughput and scalability.
- Leaf Layer: Connects servers (CX7 NICs), handling primarily north-south traffic.
- Spine Layer: Connects multiple Leaf switches and carries east-west traffic.
- 1:1 Oversubscription Ratio: The number of optical transceivers at the Leaf layer is twice that of the Spine layer, ensuring non-blocking performance.
Deployment Example:
- Spine Switches (NVIDIA 9790/9700): Equipped with 800G OSFP 2×SR4 optical transceivers.
- Leaf Switches (NVIDIA 9790/9700): Also use 800G OSFP 2×SR4 transceivers to connect to GPU servers.
- GPU Servers (CX7 NICs): Use 400G OSFP SR4 (flat top) optical transceivers to connect to Leaf switches.
4. Mass Production and Application Validation
- The 800G OSFP 2×SR4 and 400G OSFP SR4 optical transceivers have entered full-scale mass production.
- Shipped in large volumes and validated by customers for stable quality and reliable performance.
- Widely deployed in AI computing clusters, HPC environments, and hyperscale data centers. Continued technical optimization will drive the evolution of AI networking infrastructure.




