The relentless expansion of data traffic—fueled by artificial intelligence, machine learning, cloud computing, and high-definition streaming—has placed immense pressure on existing network infrastructure. Data centers, hyperscalers, and telecom operators are constantly seeking solutions that can significantly boost capacity while simultaneously managing escalating operational costs. This imperative has thrust the 800G transceiver into the spotlight as the next-generation workhorse. However, the pursuit is not merely for raw speed; rather, it is for low price 800G transceiver solutions that deliver both performance and substantial economic value.
The Rise of 800G and the Demand for Cost Efficiency

The leap from 400G to 800G transceiver technology represents a critical juncture in optical networking. The sheer volume of data being moved today demands a doubling of bandwidth density, and the 800G transceiver provides this essential throughput. Yet, initial deployment costs for cutting-edge technology can be prohibitive, often slowing down the necessary pace of infrastructure upgrades. Consequently, the market is intensely focused on low price 800G transceiver modules—those that can democratize this speed increase without financially crippling IT budgets.
This transition is underpinned by significant advances in silicon photonics and signal processing. By leveraging sophisticated modulation techniques, such as PAM4 (Pulse Amplitude Modulation-4), 800G modules achieve higher bit rates without proportional increases in power consumption or physical size. The development of competitive, multi-sourced components and standardized form factors like QSFP-DD800 (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable Double Density 800) and OSFP (Octal Small Form-factor Pluggable) is driving down manufacturing costs. Ultimately, this competitive landscape is the primary engine behind the emergence of the low price 800G transceiver. This affordability allows network architects to plan for large-scale, cost-effective deployments, ensuring the network can handle the insatiable demand for bandwidth over the coming years.
Essential Features and Technical Underpinnings
A truly valuable low price 800G transceiver must not compromise on core technical specifications. Its features must align with the demanding environments of modern data centers.
Power Efficiency: The Hidden Cost Saver
One of the most critical features in the total cost of ownership (TCO) calculation for optical modules is power consumption. In a hyperscale data center where tens of thousands of transceivers are deployed, a small reduction in power per module translates into massive savings on energy and cooling costs. The latest generation of low price 800G transceiver modules are engineered to achieve superior power efficiency, often utilizing advanced CMOS process nodes for their digital signal processors (DSPs) and minimizing optical component loss. Achieving a lower operating power is, therefore, integral to the value proposition of a low price 800G transceiver, moving beyond the initial purchase price to long-term operational savings.
Reliability and Standardization for Seamless Integration
For an upgrade to be successful, the new modules must integrate seamlessly with existing or newly deployed network hardware. This is where standardization, particularly with the QSFP-DD800 and OSFP form factors, becomes essential. OpticTran’s commitment to these industry-standard footprints ensures that its low price 800G transceiver products are plug-and-play ready, minimizing installation complexity and potential compatibility issues. Furthermore, product reliability, often measured by mean time between failures (MTBF), is paramount. A module that is cheaper to buy but prone to failure incurs high maintenance costs and significant downtime. The most attractive low price 800G transceiver achieves its cost reduction through manufacturing efficiencies and scale, not through the use of inferior components.
Reach and Application Versatility
The utility of any optical module depends heavily on its reach. Low price 800G transceiver modules are typically designed for diverse applications, from short-reach connections within a data center rack (e.g., using VCSEL or MMF technology for distances up to 60 meters) to medium-reach links between buildings or across campus networks (e.g., using DR8 or LR8 for distances up to 2km or 10km over single-mode fiber). The availability of various reaches at an accessible price point allows network engineers to precisely match the module to the required link, thereby optimizing fiber utilization and avoiding the unnecessary expense of over-specified optics.
Market Impact and Strategic Value for Optical Module Users
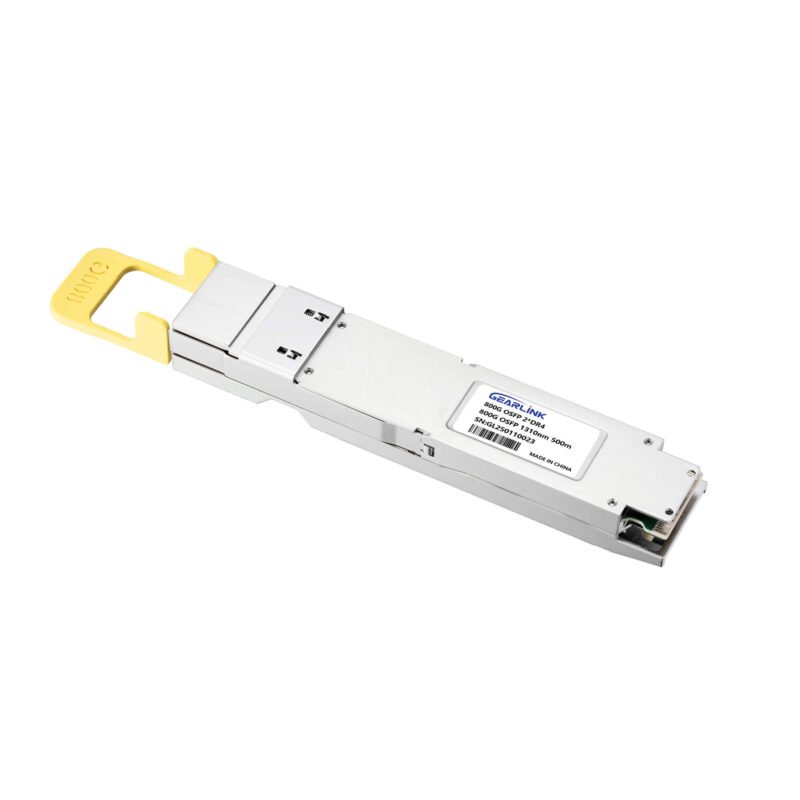
800GBASE 2 x DR4/DR8 OSFP PAM4 1310nm 500m DOM Dual MPO-12/APC SMF Optical Transceiver Module
Price range: NT$1,699 through NT$1,768
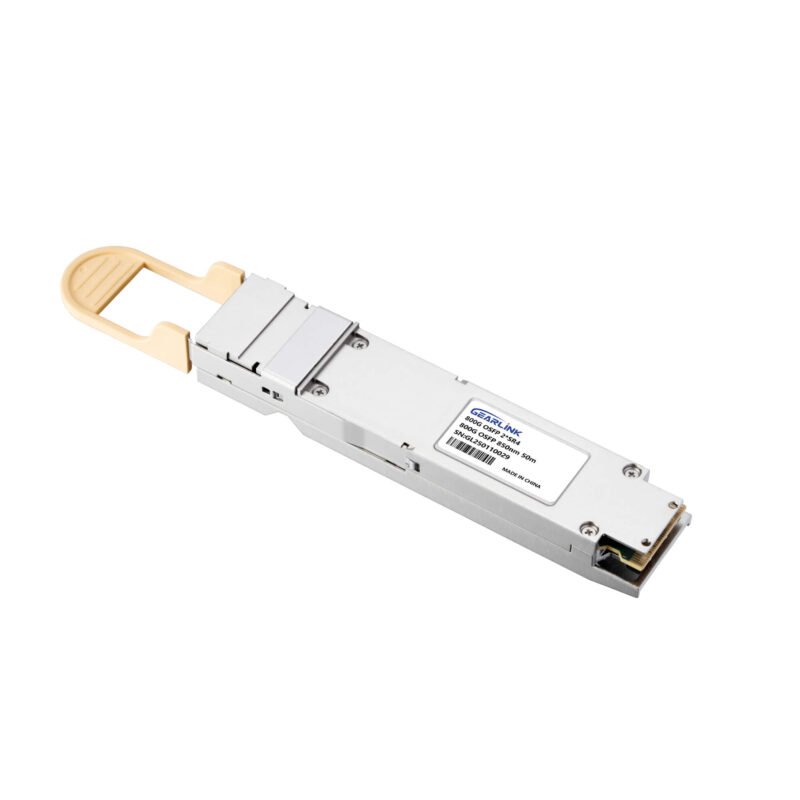
800G OSFP SR8-800GBASE 2 x SR4/SR8 OSFP PAM4 850nm 50m DOM Dual MPO-12/APC MMF InfiniBand NDR Optical Transceiver Module
Price range: NT$539 through NT$808
The availability of the low price 800G transceiver is fundamentally changing the calculus of network investment for optical module users—data center owners, enterprise networking professionals, and system integrators.
Accelerating the Network Refresh Cycle
Previously, the cost of the latest high-speed optics often meant a multi-year lag before widespread adoption. The advent of the low price 800G transceiver significantly shortens this refresh cycle. Organizations can now justify upgrading from 200G or 400G sooner, directly addressing bottlenecks and capacity constraints before they impact service quality. This acceleration is crucial for competitive advantage in sectors where bandwidth is a direct determinant of performance, such as financial trading, AI model training, and content delivery. A low price 800G transceiver acts as a catalyst, making the once-aspirational 800G ecosystem an immediate and practical reality.
Enhanced Port Density and Infrastructure ROI
By offering a high-density solution in compact form factors, low price 800G transceiver modules maximize the throughput available per rack unit (RU) of switch and router equipment. For example, a switch designed for QSFP-DD slots can double its faceplate bandwidth when upgrading from 400G to 800G. This increase in port density provides a substantial return on investment (ROI) on the core networking hardware. Instead of adding more physical switches—which consume more power, space, and cooling—operators can increase capacity simply by upgrading the optical modules. This strategy is not just about saving money on optics; it is about extending the useful life and maximizing the value of the entire network fabric.
Driving Interoperability and Open Networking
The push for cost efficiency often aligns with the move towards open networking and multi-vendor interoperability. As more manufacturers compete to offer a low price 800G transceiver, adherence to industry standards and rigorous testing for compatibility becomes non-negotiable. This benefits the end-user by reducing vendor lock-in and allowing them to source the best-performing and most economically viable components from various suppliers. OpticTran contributes to this healthy ecosystem by ensuring its low price 800G transceiver products are fully interoperable, giving users the freedom and flexibility to design truly optimized, best-of-breed networks. This open approach fosters a more competitive and innovative market overall.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Affordable High-Speed Optics
The journey toward 800G is a staging ground for the next frontier: 1.6T and beyond. The technology innovations that make a low price 800G transceiver possible—especially in photonics integration, advanced packaging, and DSP optimization—will be the foundation for future generations of high-speed optics.
For optical module users, the critical takeaway is that the market has matured to a point where high performance no longer equates to a prohibitively high cost. The low price 800G transceiver is not a temporary anomaly but a new, sustainable market reality driven by technological maturity and robust competition. Strategically, this means network planners must now prioritize total value—a combination of purchase price, power efficiency, reliability, and guaranteed interoperability—when making procurement decisions.
Ultimately, the choice to adopt the low price 800G transceiver is a choice to build a future-ready, scalable, and economically sound network infrastructure. It is the intelligent path forward for meeting the exponential growth in global data demand without sacrificing fiscal responsibility. By embracing these affordable, high-performance solutions, organizations can ensure they remain at the forefront of digital transformation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the main difference between a standard 800G transceiver and a low price 800G transceiver?
The primary difference lies in the economies of scale, manufacturing optimization, and vendor competition, not a compromise on core technical standards (like data rate or form factor). A high-quality low price 800G transceiver achieves cost reduction through mature, high-volume production processes and efficient component sourcing while still adhering to industry specifications for performance, power, and interoperability.
Q2: What form factors are most common for low price 800G transceiver modules?
The most common and competitive form factors driving affordability are QSFP-DD800 and OSFP. Both allow for high port density and are widely supported by major networking equipment vendors, which is a key factor in driving down overall market cost.
Q3: How does the low price 800G transceiver help with power consumption in a data center?
The competitive drive for a low price 800G transceiver includes minimizing its power consumption. Lower power usage directly translates to lower operational costs (OPEX) for electricity and cooling. Modern 800G modules leverage advanced silicon photonics and highly integrated DSPs to deliver 800G speed with industry-leading power efficiency, making them excellent long-term investments.
Q4: Are low price 800G transceiver modules compatible with my existing 400G or 200G equipment?
This depends on your switch or router. Generally, 800G modules, particularly those in the QSFP-DD800 form factor, are designed to be backward compatible and can often operate in lower-speed modes (like 2x400G or 8x100G breakout modes) with the right host hardware configuration. However, full compatibility should always be verified with the equipment vendor.