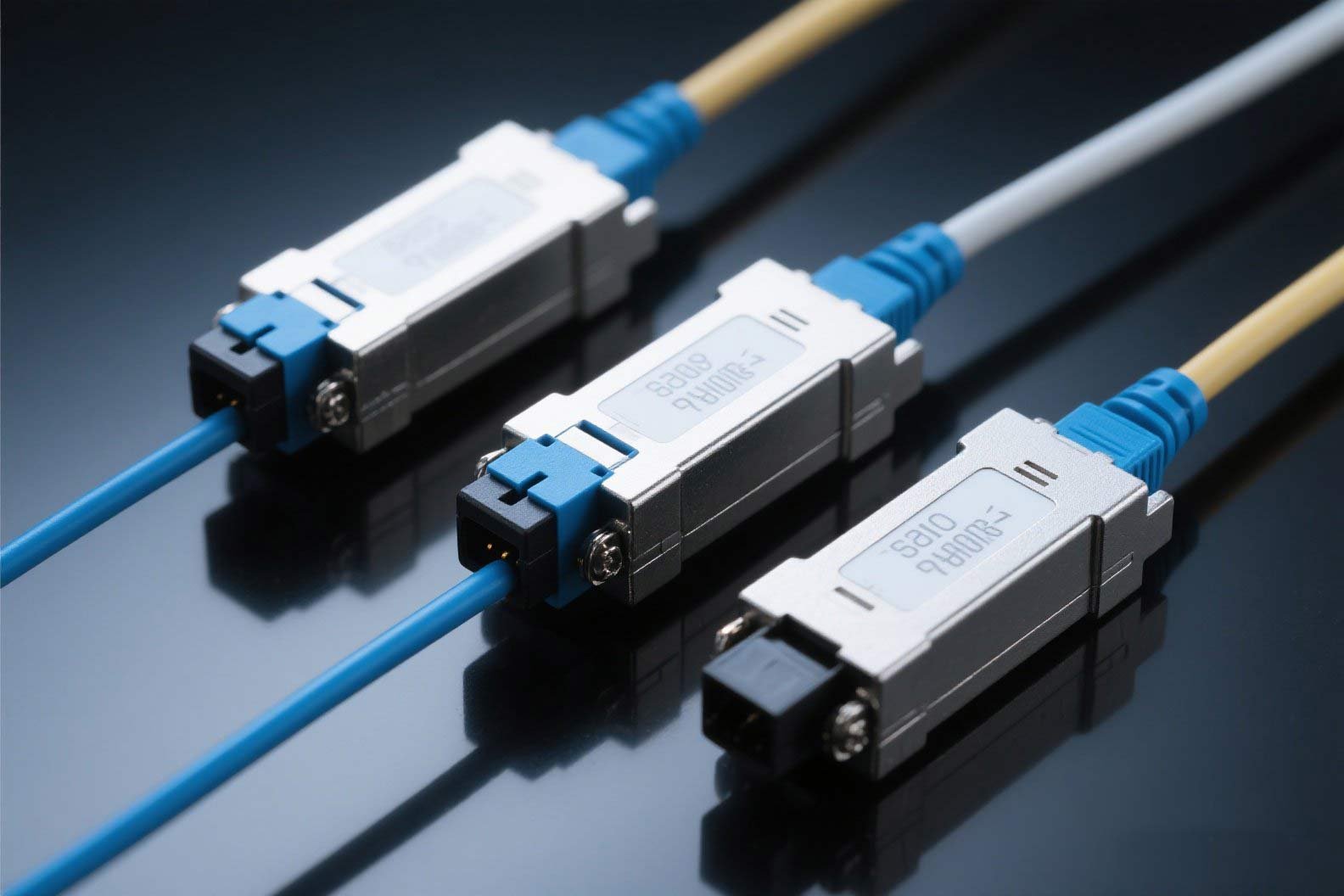
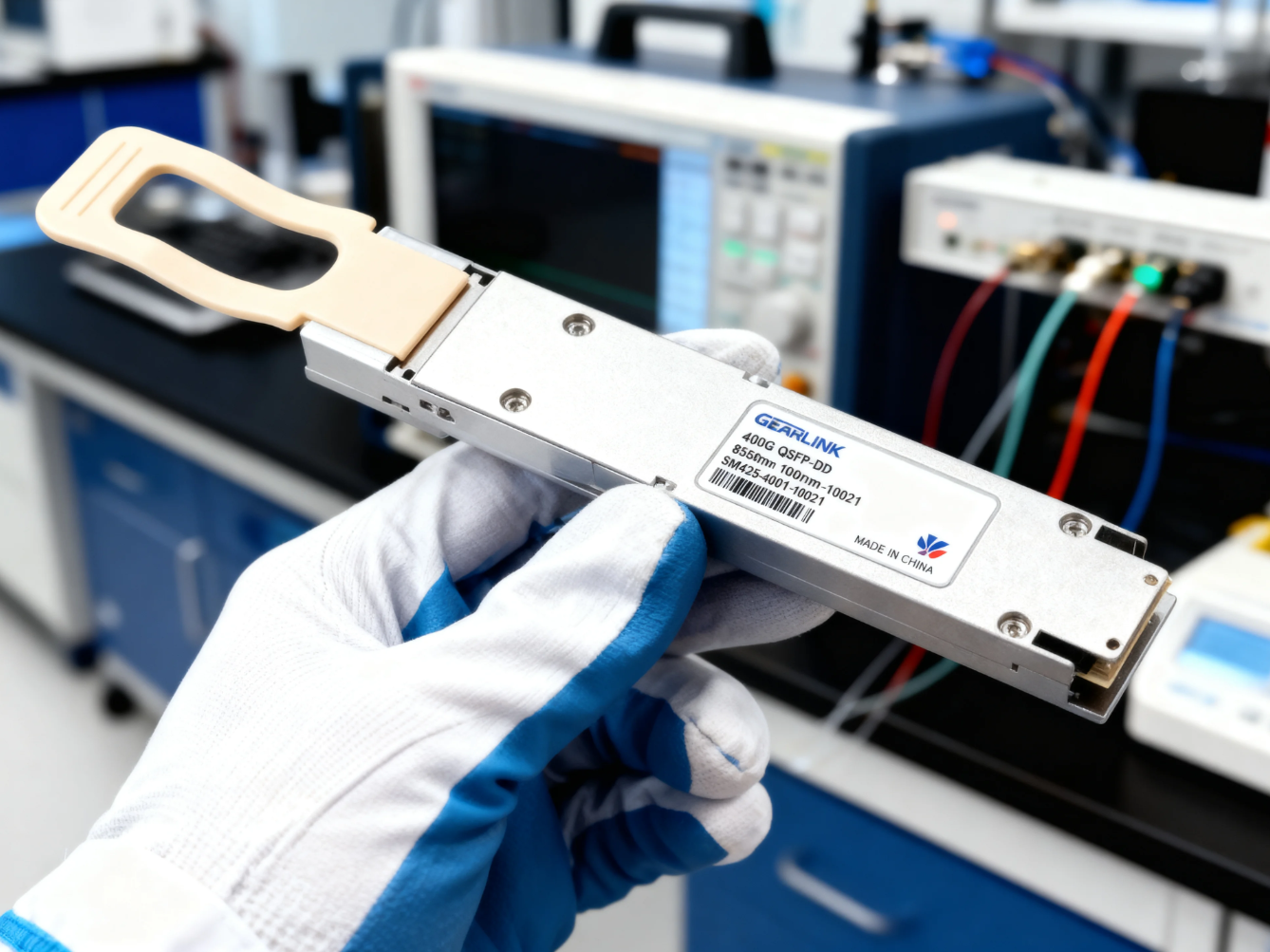
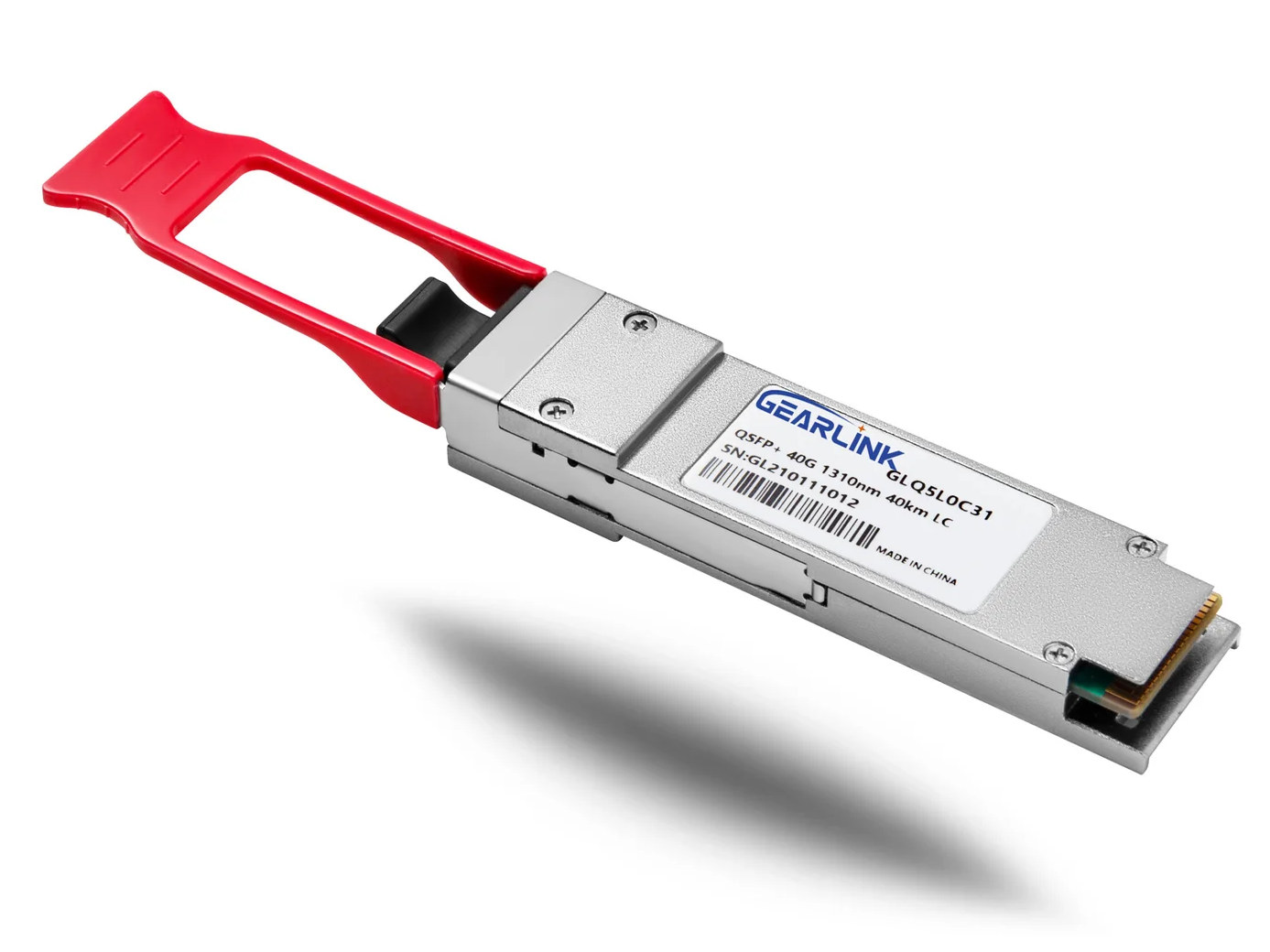
Introduction: Why Optical Transceivers Matter in Today’s Networking
In the fast-evolving world of telecommunications and networking, optical transceivers play a crucial role in ensuring high-speed, efficient data transmission across vast distances. These compact devices enable the conversion of electrical signals into optical signals, which can travel much faster and farther over fiber-optic cables. If you’re a network operator, IT professional, or telecom service provider in the United States, understanding the importance of optical transceivers can dramatically enhance your infrastructure’s performance.
This article will dive into the core advantages and features of optical transceivers, providing a comprehensive overview for professionals in the U.S. optical transceiver market. We will cover their functionality, how they contribute to faster network speeds, and why they’re the backbone of modern communication systems.
What is an Optical Transceiver?
An optical transceiver is an integrated circuit that converts electrical signals into optical signals (and vice versa) for the purpose of data transmission over fiber-optic cables. These devices are a critical component in any modern fiber-optic network, enabling efficient communication over long distances without significant signal loss or degradation.
There are various types of optical transceivers, including Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP), SFP+, XFP, and QSFP, each tailored to specific applications, including data centers, enterprise networks, and telecommunications.
Key Features of Optical Transceivers

1. High-Speed Data Transmission
One of the most significant advantages of optical transceivers is their ability to facilitate extremely high-speed data transfer. With the rapid rise of data traffic globally, especially in the U.S., high-speed data transmission is critical. Optical transceivers support speeds of 10 Gbps, 40 Gbps, 100 Gbps, and even beyond, enabling networks to meet the demands of modern digital services like cloud computing, big data analytics, and video streaming.
2. Long-Distance Transmission with Minimal Signal Loss
Another advantage of using optical transceivers is their ability to transmit data over long distances with minimal signal loss. Fiber-optic cables, unlike traditional copper wires, can carry signals across several kilometers without significant degradation. This feature is especially important in large-scale networks and data centers that require consistent, reliable communication over great distances.
3. Low Latency
For real-time communication applications, such as VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol), video conferencing, or online gaming, low latency is essential. Optical transceivers offer minimal delay in data transmission, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted communication. This makes them a preferred choice for industries where speed and efficiency are paramount.
4. Scalability
As demand for bandwidth continues to grow, optical transceivers provide the scalability needed to future-proof networks. They allow for easy upgrades to higher speeds, which is essential for companies planning to scale their network infrastructure. With optical transceivers, businesses can adapt to increasing data traffic without overhauling their entire network.
5. Energy Efficiency
Optical transceivers are designed to be energy-efficient compared to their copper counterparts. As energy costs continue to rise, this is an important feature for companies looking to reduce their operating costs. The efficiency of optical transceivers helps to lower power consumption while maintaining high performance, making them an environmentally friendly solution.
Types of Optical Transceivers and Their Applications
1. SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable) Transceivers
SFP transceivers are widely used for short- and medium-range communication. They are commonly found in enterprise networks and are compatible with various fiber-optic cables. These transceivers are popular for their compact size and versatility.
2. SFP+ Transceivers
An upgrade of the standard SFP, SFP+ supports speeds of up to 10 Gbps, making them ideal for data centers and high-performance computing applications. They are designed for high-speed data transmission over short distances.
3. QSFP (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable) Transceivers
QSFP transceivers support multi-lane data transmission, offering higher speeds of up to 100 Gbps. They are widely used in data centers, high-performance computing, and telecommunications networks where large volumes of data need to be processed at high speeds.
4. XFP Transceivers
XFP transceivers are designed for high-speed applications and long-distance transmission. They are often used in telecommunications, providing reliable and efficient data transfer over fiber-optic networks.
The Importance of Optical Transceivers in Data Centers and Telecom Networks
In the United States, data centers and telecom networks require cutting-edge technology to keep up with the ever-growing demand for fast and reliable communication. Optical transceivers are integral to meeting this demand. They form the backbone of modern data centers, ensuring that large amounts of data can be transmitted quickly and efficiently between servers, routers, and switches.
Benefits for Data Centers:
- Faster Data Processing: Optical transceivers help minimize delays in data transmission, enabling faster processing speeds and improving overall performance.
- Efficient Space Utilization: The compact size of optical transceivers allows data centers to maximize available space, which is especially important as data center infrastructure grows.
- Reduced Infrastructure Costs: With optical transceivers, data centers can reduce the need for expensive, power-hungry copper-based solutions.
Benefits for Telecom Networks:
- High-Speed Connectivity: Telecom networks rely on optical transceivers for high-speed connectivity, which is essential for maintaining competitive edge in the market.
- Reliability and Uptime: These transceivers ensure that telecom networks can maintain consistent uptime, even during peak usage times.
- Long-Distance Connectivity: Optical transceivers are critical for connecting telecom infrastructure across cities, states, and countries, facilitating communication over long distances.
Why Choose Optical Transceivers for Your Networking Needs?
Incorporating optical transceivers into your network infrastructure is an investment in future-proofing your system. With the increasing need for faster speeds, lower latency, and scalable solutions, optical transceivers are the ideal choice for anyone looking to upgrade their telecommunications or data center capabilities.
Considerations for Choosing the Right Optical Transceiver
When selecting an optical transceiver, several factors should be considered:
- Compatibility: Ensure that the transceiver is compatible with your existing equipment.
- Speed Requirements: Choose a transceiver that supports the required speeds for your network.
- Distance: Consider the distance over which the data needs to travel, as this will determine the type of transceiver to use.
Conclusion: The Future of Networking Lies in Optical Transceivers
The demand for faster, more reliable, and scalable network solutions continues to rise, making optical transceivers a key technology in the telecommunications and data center industries. By offering high-speed data transmission, long-distance communication, low latency, and energy efficiency, optical transceivers are essential for staying competitive in today’s fast-paced digital world.
For businesses in the U.S., investing in high-quality optical transceivers will enable you to build robust, future-ready network infrastructure that meets the demands of modern communication.