As data traffic continues to grow exponentially, driven by cloud computing, AI, 5G, and high-performance applications, the demand for high-speed and high-density interconnects in data centers has never been greater. Among various optical transceiver form factors, the 400G QSFP-DD (Quad Small Form Factor Pluggable Double Density) has emerged as the most widely adopted solution, providing the necessary performance, scalability, and energy efficiency for next-generation networks.
1. Overview of 400G QSFP-DD Optical Transceivers
The 400G QSFP-DD optical transceiver is designed to support 400 Gigabit Ethernet transmission in high-density environments. Building on the widely used QSFP form factor, QSFP-DD adds a second row of electrical contacts, doubling the number of high-speed lanes from 4 to 8. This enables the module to support up to 8 x 50Gbps or 8 x 53Gbps PAM4 signals, achieving an aggregate bandwidth of up to 400Gbps.
Thanks to its compact size and backward compatibility with QSFP28 and QSFP56, QSFP-DD has become the preferred interface for large-scale deployments in data centers and telecom networks. It supports a wide range of transmission distances and media types, from multimode fiber for short-reach to single-mode fiber for long-distance links.
2. Main Types of 400G QSFP-DD Optical Transceivers
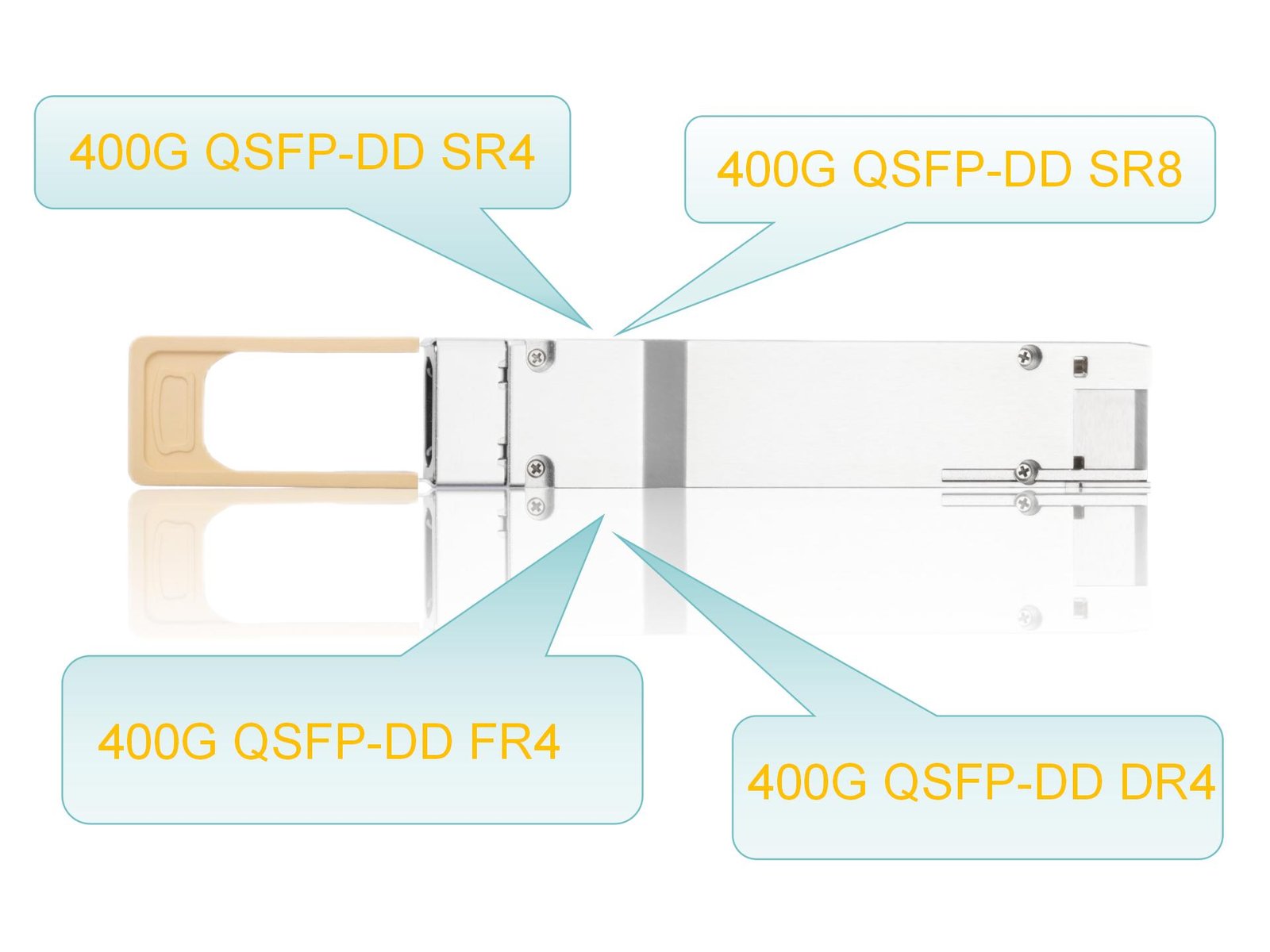
There are several types of 400G QSFP-DD optical transceivers designed for different transmission distances and applications. Among them, four of the most common models are:
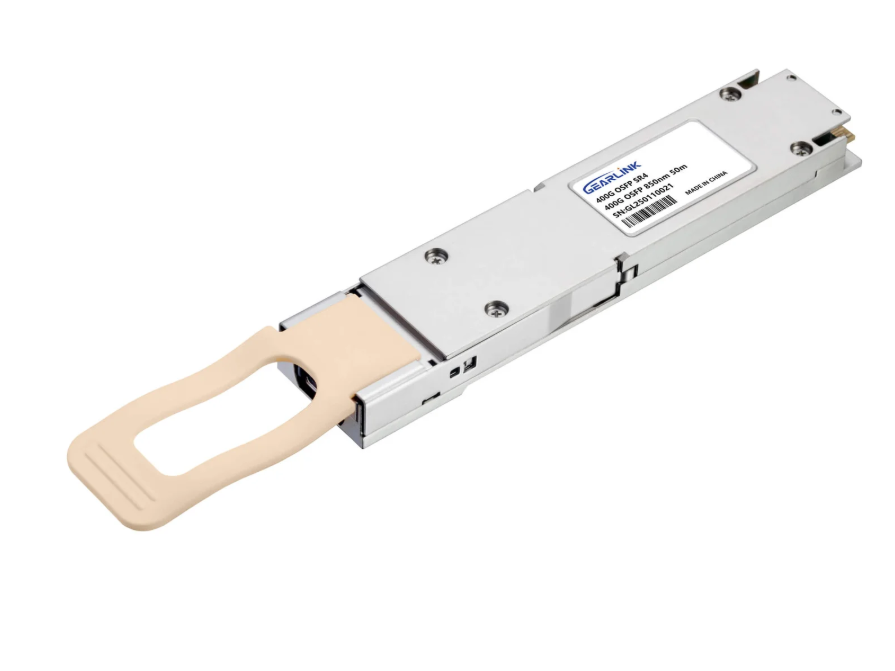
400G QSFP-DD SR8: This is a multimode optical transceiver that operates over OM4 fiber. It uses 8 parallel channels at 50Gbps each, supporting transmission distances up to 100 meters. It is commonly used for high-density short-reach interconnects within data centers.
400G QSFP-DD SR4: Also based on multimode fiber, this module uses 4 optical channels of 100Gbps each. While less common than SR8, it serves similar short-reach applications and offers simplified cabling compared to 8-channel solutions.
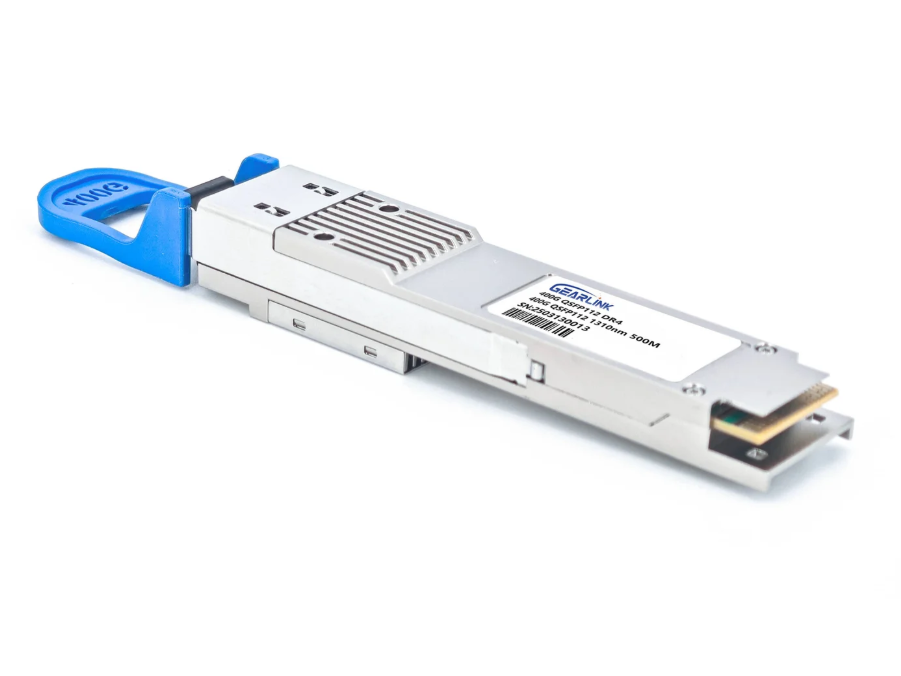
400G QSFP-DD DR4: A single-mode optical transceiver that transmits 4 x 100Gbps over 500 meters using parallel single-mode fiber. It is widely used for medium-reach data center interconnects and is compatible with breakout configurations to 4 x 100G DR links.
400G QSFP-DD FR4: This single-mode module uses four wavelengths over a single fiber (CWDM technology), supporting distances up to 2 kilometers. It is ideal for longer intra-data center or short inter-data center connections.
3. Key Differences Between Common QSFP-DD Transceivers
Understanding the technical differences between similar models helps network architects make informed decisions:
3.1 400G QSFP-DD SR8 vs. 400G QSFP-DD SR4
The key difference lies in the number of optical lanes. SR8 uses 8 parallel multimode fibers (50Gbps each), while SR4 uses 4 fibers transmitting at 100Gbps. SR8 typically offers better scalability for breakout configurations (e.g., 8 x 50G or 8 x 100G) and is more suitable for applications requiring greater port flexibility. SR4, on the other hand, simplifies fiber management and may reduce cable bulk, though it is less common in 400G deployments.
3.2 QSFP-DD DR4 vs. QSFP-DD FR4
Both are used for single-mode applications, but they differ significantly in design and reach. DR4 uses 4 parallel optical fibers, each transmitting at 100Gbps over up to 500 meters, and is mainly used in point-to-point connections inside data centers. FR4, however, multiplexes four wavelengths (CWDM) onto a single fiber pair, enabling transmission up to 2km. FR4 offers advantages in reducing fiber count and is well-suited for scenarios where fiber resources are limited or longer distances are required.
4. Application Scenarios of 400G QSFP-DD Optical Transceivers
The primary application for 400G QSFP-DD optical transceivers is high-speed data center interconnects. As cloud service providers and hyperscale data centers continue to scale infrastructure, 400G transceivers are deployed to support bandwidth-intensive applications, AI/ML workloads, and scalable spine-leaf network architectures.
Intra-data center connectivity: SR8 and SR4 modules are mainly used for short-reach interconnects, such as server-to-switch or switch-to-switch connections within the same rack or across adjacent racks.
Medium-distance connections: DR4 modules are suitable for interconnecting different rows or zones within the same data center, offering a balance of performance and cost over single-mode fiber.
Longer-reach intra-campus links: FR4 modules support distances up to 2km, making them ideal for data center to aggregation switch connections or between data center buildings within a campus. By offering a range of transmission options with a unified interface, QSFP-DD optical transceivers provide data center operators with the flexibility and scalability needed to future-proof their networks.