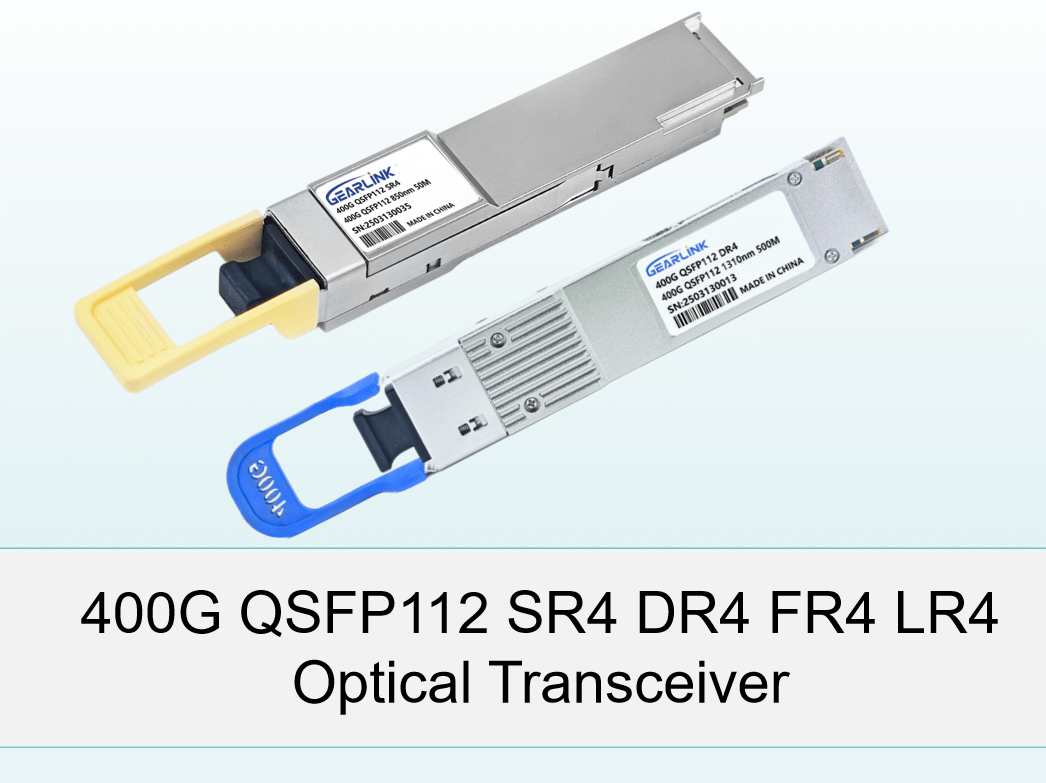
The term “QSFP112” is derived from the combination of “Q,” which signifies the 4-channel configuration of the transceiver, and “SFP112,” referring to its speed—making it quite easy to remember. Specifically, the QSFP112 optical transceiver represents a 400G optical transceiver, consisting of 4 channels, each operating at 100G. This modular configuration is designed to meet the ever-increasing demands for higher bandwidth in modern data centers and telecommunication networks.
Comparatively, QSFP56 and QSFP28 represent lower bandwidth optical transceivers. The QSFP56 supports 4 channels operating at 50G each, providing a total of 200G bandwidth. Similarly, QSFP28 supports 4 channels at 25G, offering a total of 100G bandwidth. These earlier generations of QSFP transceivers have paved the way for the development of the more advanced QSFP112, which is specifically tailored for the 400G ecosystem.
What is the QSFP112 Optical transceiver?
The QSFP112 optical transceiver is a cutting-edge interconnect solution designed to support 400G speeds in a compact 4-channel Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) design. It is built upon the proven QSFP design, which has been a mainstay in high-performance networking for years. The primary innovation of the QSFP112 is its ability to support 112 Gb/s per channel, allowing it to deliver an aggregate bandwidth of 400G.
This next-generation optical transceiver is a vital component in the development of high-speed data networks. It is designed to support 400G Ethernet, InfiniBand, and Fibre Channel protocols, making it an essential building block for modern data center architectures. The QSFP112 transceiver enables organizations to upgrade from previous generations of QSFP technologies, such as QSFP28 or QSFP56, with minimal disruption, providing a seamless transition to the 400G ecosystem.
The transceiver’s electrical architecture uses cutting-edge PAM4 (Pulse Amplitude Modulation 4-level) and other advanced modulation techniques to achieve high data rates. Compared to previous generations, the QSFP112 transceiver reduces power consumption by nearly 30%, offering a more energy-efficient solution for data centers that require high-speed, low-latency interconnections.
What are the Advantages of the QSFP112 Optical transceiver?
High-Speed Performance:
The most significant advantage of the QSFP112 optical transceiver is its ability to support up to 400 Gbps data rates. This high-speed capability is essential for modern data centers that need to handle vast amounts of data. With the increasing adoption of cloud computing, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and 5G technologies, the demand for faster and more efficient data transmission is skyrocketing. The QSFP112 meets these demands, providing the necessary bandwidth for next-generation applications and services.
Low Power Consumption:
Energy efficiency is a critical factor in data center operations, where power consumption can be a major operational cost. The QSFP112 is designed to consume significantly less power compared to its predecessors, offering up to 3.5W lower power consumption than other 400G transceivers. This is achieved through advancements in the transceiver’s electrical and optical designs, ensuring that it not only delivers exceptional performance but does so in an energy-efficient manner. For data center operators seeking to minimize their carbon footprint and operating expenses, the QSFP112 offers a compelling solution.
Enhanced Signal Integrity and Reduced EMI:
Signal integrity is paramount in high-speed optical transceivers, where even minor distortions can lead to data errors or degraded performance. The QSFP112 employs a combination of advanced signal processing techniques and optimized hardware to ensure that signal quality is maintained at peak performance levels. Additionally, the transceiver’s design minimizes electromagnetic interference (EMI), making it ideal for deployment in high-density environments like data centers, where numerous devices are operating in close proximity to one another.
Broad Compatibility:
Another key advantage of the QSFP112 is its broad compatibility with a variety of existing networking protocols. The transceiver supports Ethernet, InfiniBand, and Fibre Channel protocols, making it suitable for a wide range of use cases across different industries. Furthermore, it is fully compatible with previous generations of QSFP transceivers, such as QSFP28 and QSFP56, enabling seamless upgrades and integration into existing infrastructures. This backward compatibility ensures that organizations can transition to 400G speeds without needing to replace their entire network infrastructure.
Cost-Effectiveness:
While the QSFP112 transceiver provides high-performance capabilities, it is also designed to be cost-effective. By reducing the number of electrical connections required and simplifying the production process, the QSFP112 lowers unit costs compared to previous transceivers like the QSFP-DD. This cost reduction makes it an attractive option for organizations looking to scale their network infrastructure while keeping costs in check.
Types of QSFP112 Optical transceivers: SR4, DR4, FR4, and LR4
The QSFP112 optical transceiver comes in four primary types, each optimized for different applications based on transmission distance and media type. These are:
SR4 transceiver (Short-Range):
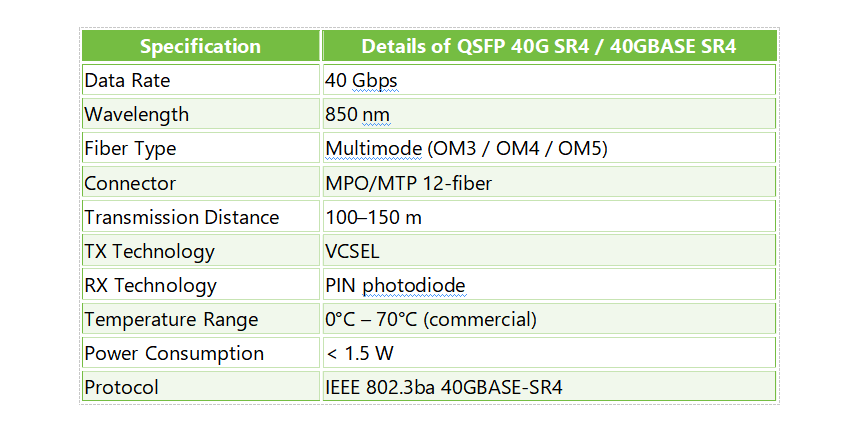
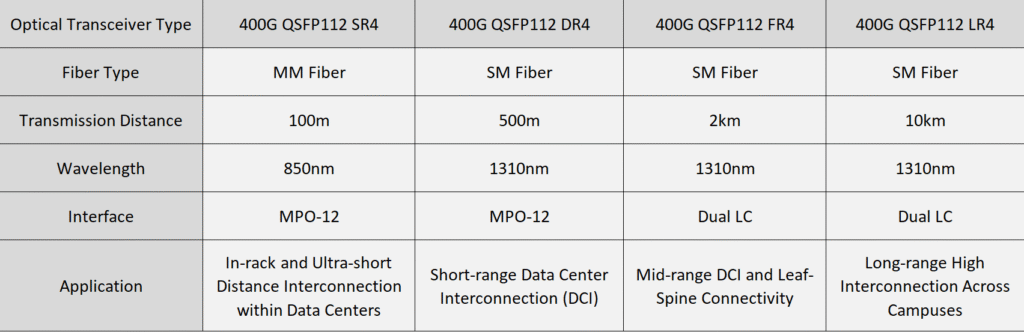
The SR4 transceiver is designed for short-distance, multimode fiber (MMF) applications. It uses VCSEL (Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser) technology for parallel 4×100G PAM4 transmission over OM3 or OM4 multimode fiber. The SR4 transceiver can support transmission distances of up to 100 meters. It is ideal for high-density data center environments where short-range interconnections are required. The SR4 transceiver is also known for its low power consumption, typically below 8W.
DR4 transceiver (Long-Range):
The DR4 transceiver is based on single-mode fiber and supports transmission over longer distances, up to 500 meters. It uses a 1310 nm wavelength for its four parallel channels. This transceiver is equipped with EML (Electro-absorption Modulated Laser) lasers and an MPO-12 connector for high-speed data transmission. The DR4 transceiver is an excellent choice for long-range data center connections, especially when low power consumption is a priority. It can also be configured with a Linear Pluggable Optical (LPO) architecture, reducing power consumption to below 6W.
FR4 transceiver (Extended Range):
The FR4 transceiver utilizes CWDM4 (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) to transmit data over distances of up to 2 kilometers using duplex single-mode fiber (OS2). It operates across a range of wavelengths from 1270 nm to 1330 nm. The FR4 transceiver is well-suited for mid-range data center interconnections, particularly in spine-leaf architectures, where higher bandwidth and reduced latency are essential.
LR4 transceiver (Long-Range):
The LR4 transceiver is designed for long-distance transmission, supporting distances of up to 10 kilometers over single-mode fiber. It uses CWDM4 wavelength division multiplexing technology, with high-performance EML lasers to achieve the necessary reach. The LR4 transceiver is ideal for interconnecting data centers over large geographical areas, such as across campus networks or between regional data centers. It typically operates with a power consumption of 12-14W, providing a reliable solution for long-distance, high-speed data transmission.
Comparison of QSFP112 Optical transceiver with Other transceiver Types
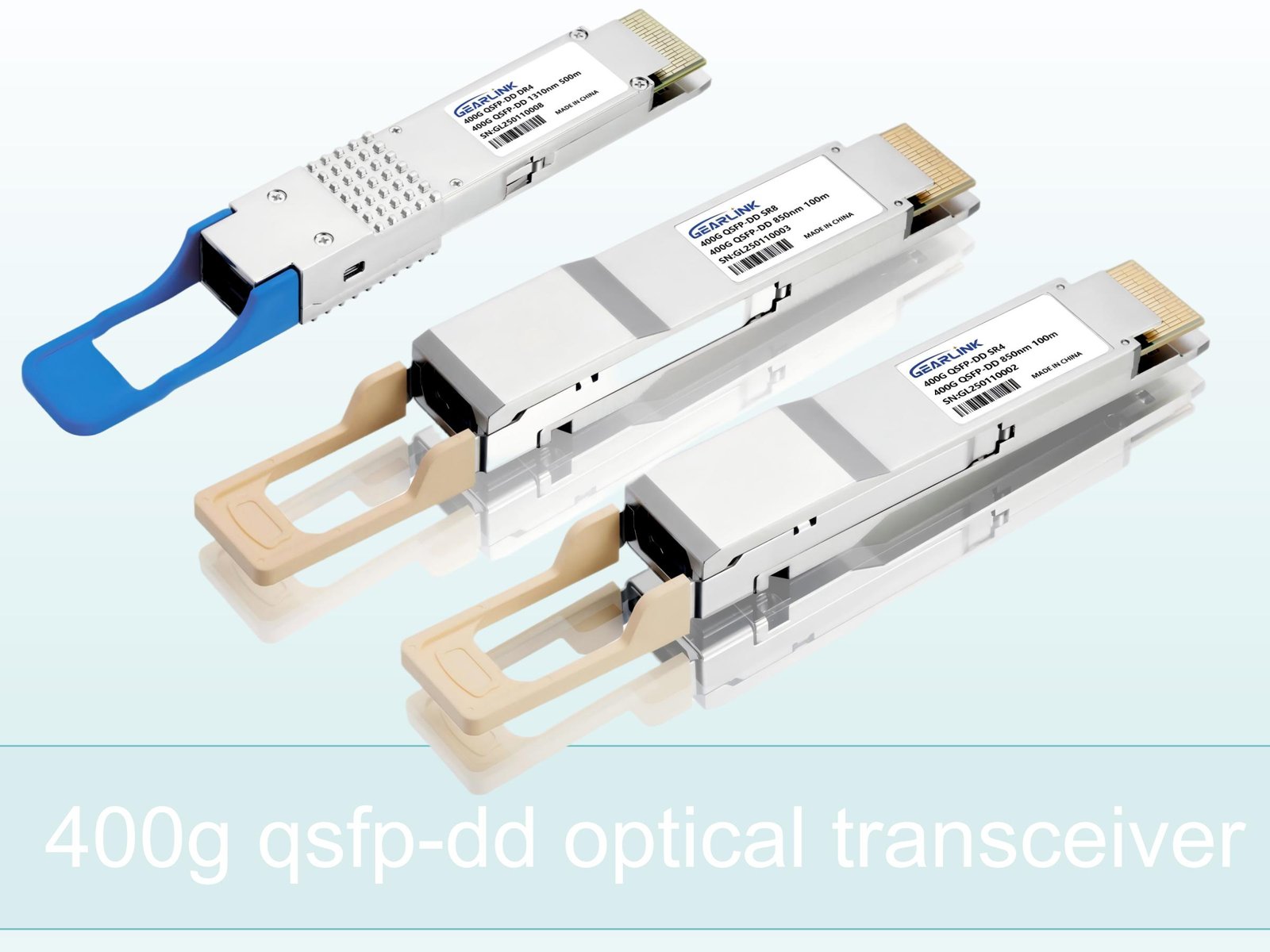
QSFP112 vs. QSFP-DD:
The QSFP112 and QSFP-DD optical transceivers are similar in many respects but differ primarily in their data rate, size, and scalability. The QSFP112 supports up to 400 Gbps, utilizing PAM4 and other advanced modulation techniques. It is compatible with earlier generations of QSFP transceivers, such as QSFP28 and QSFP56.
In contrast, the QSFP-DD optical transceiver supports 800 Gbps through an 8-channel design, offering higher scalability and density. This allows for more ports to be packed into the same physical space, making the QSFP-DD ideal for applications that require massive bandwidth aggregation.
Differences Between 400G QSFP112 and QSFP28
The 400G QSFP112 and QSFP28 optical transceivers differ in data rate, modulation technology, and use cases. The QSFP112 uses PAM4 and other advanced modulation technologies to support up to 400 Gbps. On the other hand, the QSFP28 uses NRZ (Non-Return-to-Zero) modulation, which limits its maximum speed to 100 Gbps. The QSFP112 is designed for high-bandwidth applications, whereas the QSFP28 is often used in 100G Ethernet networks requiring reliable, cost-effective transmission.
How Does the 400G QSFP112 Transceiver Compare to the QSFP-DD800 transceiver?
While the 400G QSFP112 supports up to 400 Gbps, the QSFP-DD800 optical transceiver can deliver up to 800 Gbps—double the capacity of the former. The QSFP-DD800 is designed for next-generation high-density applications that demand even higher bandwidth and port density, making it an ideal choice for large-scale data center environments.