The insatiable demand for network capacity within hyperscale and enterprise data centers necessitates a continuous evolution of optical interconnect technology. As network speeds transition from 100 Gigabit Ethernet (100GbE) to 400 Gigabit Ethernet (400GbE), the industry requires compact, power-efficient, and high-density transceivers to manage the sheer volume of traffic between servers and Top-of-Rack (ToR) switches. In this critical short-reach domain, the 400G QSFP-DD SR8 module has emerged as a powerhouse solution. This specific module combines a high-density form factor with a parallel optics architecture tailored for Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF), making it a dominant choice for links up to 100 meters. The central question for network architects today, therefore, is: Does the 400G QSFP-DD SR8 truly represent the optimal balance of density, performance, and cost-effectiveness required for the next generation of intra-rack and inter-rack connectivity? We will explore the technical underpinnings of this module, analyze its competitive edge over other 400G solutions, and detail its strategic role in maximizing efficiency within the physical confines of the modern data center.
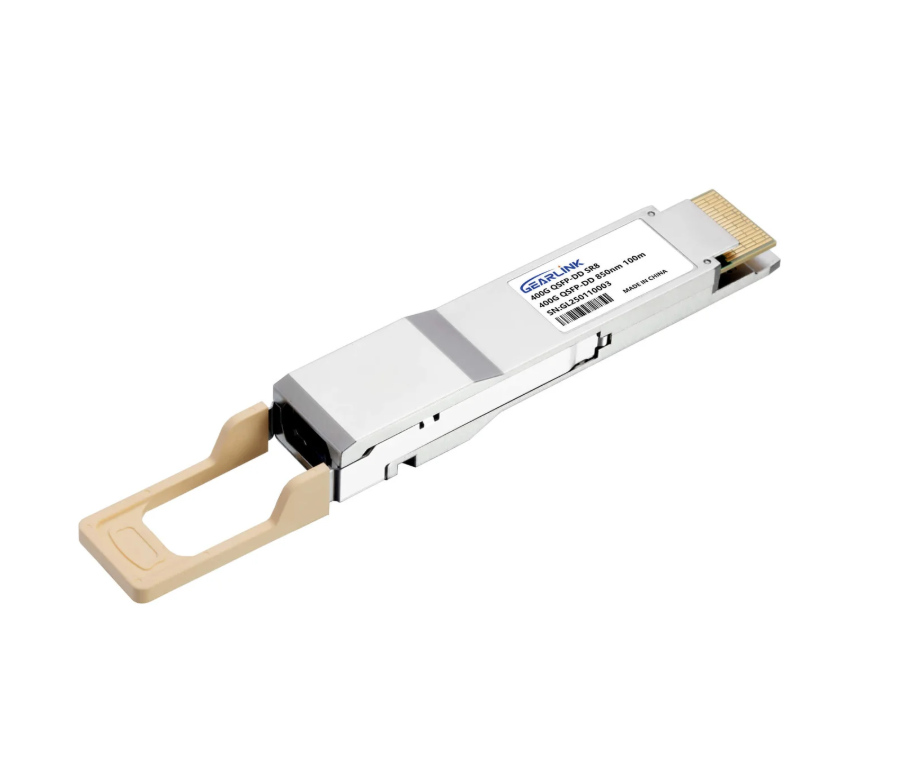
The Architecture of Density: Defining the 400G QSFP-DD SR8
The efficacy of the 400G QSFP-DD SR8 lies in the clever combination of the QSFP-DD form factor and the SR8 optical configuration, resulting in a module that is both compact and highly capable.
The QSFP-DD (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable Double Density) designation is key to its high-density appeal. This form factor doubles the electrical interface of a standard QSFP module, allowing it to support eight lanes of electrical data rather than four. This doubling of electrical connections is crucial for achieving the 400G speed in a small package. Furthermore, the ‘SR8’ designation indicates that the module utilizes Short Reach (SR) technology across eight parallel optical lanes, with each lane carrying 50Gbps of data. Operating over Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF), the 400G QSFP-DD SR8 is optimized for distances up to 100 meters. This specific configuration, leveraging MMF’s capacity for high bandwidth over short distances, minimizes both component complexity and power consumption. The resulting architecture makes the module an excellent fit for high-density deployments where space is at a premium, such as server-to-switch aggregation points within the same row or adjacent racks.
The Strategic Advantage of Parallel Optics and MMF

The choice of parallel optics and Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF) provides the 400G QSFP-DD SR8 with distinct economic and deployment advantages over single-mode alternatives in the short-reach environment.
MMF is significantly more cost-effective than Single-Mode Fiber (SMF), both in terms of the fiber itself and the supporting transceiver optics. For the high volume of short-reach links that dominate a typical data center fabric, this lower cost per link translates into massive operational savings. Moreover, the parallel 8-lane architecture simplifies the transition from 100G. The 400G QSFP-DD SR8 can be configured for “breakout” applications where a single 400G port connects to four 100G QSFP28 ports (using 4x100G SR4 breakout cables). This flexibility is paramount during phased network migration, allowing operators to fully utilize their 400G switching capacity while retaining connectivity with the vast installed base of 100G server network interface cards (NICs). Consequently, the module minimizes both the cost and the logistical complexity of upgrading the network core, making the 400G QSFP-DD SR8 an efficient pathway to higher speeds.
Thermal Management and Power Efficiency in 400G QSFP-DD SR8
400GBASE-DR4 OSFP PAM4 1310nm 500m DOM MPO-12/APC SMF Optical Transceiver Module
Price range: NT$699 through NT$799
In dense computing environments, heat dissipation and power consumption are two of the most critical factors influencing data center performance and sustainability. The design of the 400G QSFP-DD SR8 specifically addresses these challenges.
The compact QSFP-DD form factor is engineered for efficient heat removal, often featuring advanced heat sinks and thermal pads to transfer heat rapidly away from the optical components. Although the module processes 400Gbps, its reliance on proven MMF technology and 8x50G electrical lanes allows it to maintain relatively low power consumption compared to certain long-haul or coherent 400G modules. Low power usage is not only an immediate operational cost benefit but also a crucial factor in achieving high-density switch configurations. Switches can support a greater number of ports when each transceiver consumes less power, avoiding thermal overload within the rack. By prioritizing power efficiency and thermal resilience, the 400G QSFP-DD SR8 contributes directly to the overall sustainability goals and operational robustness of the data center.
The Future of Interconnects: Ensuring Scalability
Any investment in 400G technology must consider the inevitable migration to 800G. The choice of the 400G QSFP-DD SR8 form factor provides a clear, defensible path for future scalability.
The QSFP-DD form factor’s inherent double-density structure ensures it can accommodate the next generation of optics. This form factor is designed to handle the complex electronics and higher power loads necessary for 800GbE modules, which will leverage 8x100G lanes. Network architects choosing the 400G QSFP-DD SR8 today can be confident that their investment in switching gear equipped with QSFP-DD ports will remain relevant for the next generation of speed. Furthermore, the standardization provided by the QSFP-DD Multi-Source Agreement (MSA) ensures that a robust ecosystem of compatible transceivers and host devices exists, safeguarding against obsolescence and promoting vendor competition. Ultimately, the 400G QSFP-DD SR8 serves as a strategic bridge, delivering immediate 400G performance while simultaneously preparing the infrastructure for the demands of tomorrow’s AI and cloud workloads.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the maximum reach of the 400G QSFP-DD SR8?
A: The 400G QSFP-DD SR8 is optimized for short-reach applications, typically supporting links up to 100 meters when utilized with high-quality OM4 Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF).
Q2: What is the main advantage of using the SR8 configuration?
A: The SR8 configuration (8 parallel lanes) allows for breakout capability. This means one 400G port can be split into four 100G ports, which is crucial for connecting new 400G switches to the existing installed base of 100G server NICs and optimizing equipment utilization.
Q3: Is the 400G QSFP-DD SR8 used with Single-Mode or Multi-Mode Fiber?
A: The 400G QSFP-DD SR8 is designed to operate over Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF). This choice is deliberate, as MMF is more cost-effective for the short-reach distances common within a single data center hall or rack.







